Enhancing Soil Strength with Modern Reinforcement Methods

Soil stability is a key factor in construction, landscaping, and civil engineering projects. Weak or unstable soil can lead to settlement, erosion, and structural failures, resulting in increased maintenance costs and safety concerns. To mitigate these challenges, engineers and landscapers have turned to advanced reinforcement materials that improve soil performance and durability.
One of the most effective solutions for soil reinforcement is the use of geotextile fabrics. These engineered materials enhance soil strength, manage water flow, and prevent erosion, making them indispensable in modern construction practices.
Understanding Soil Instability
Soil naturally exerts both lateral and vertical pressure on structures such as retaining walls, slopes, and embankments. External factors like rainfall, freeze-thaw cycles, and heavy loads can intensify this pressure. Common problems associated with soil instability include:
• Uneven settlement and soil shifting
• Increased lateral stress on retaining walls
• Soil erosion and particle displacement
• Slope and embankment instability
Effective soil reinforcement helps control these forces, ensuring that structures remain safe and durable over time.
The Role of Geotextile Fabrics
Geotextile fabrics are synthetic materials engineered to interact with soil, improving its mechanical properties. They are versatile and serve multiple functions including reinforcement, separation, filtration, and drainage. Their permeability allows water to flow while preventing soil migration, making them highly effective for long-term soil stabilization.
Features of Geotextil Tejido
Geotextil tejido, or woven geotextile, is manufactured by interlacing fibers in a grid-like pattern. This design provides high tensile strength, low elongation, and excellent load distribution. Key advantages of woven geotextiles include:
• High strength to resist soil movement
• Minimal elongation under heavy loads
• Stability for embankments and road foundations
• Durability under environmental stress
These properties make geotextil tejido ideal for applications that require strong reinforcement and structural reliability.
Applications of Woven Geotextiles
Woven geotextiles are widely used in construction and landscaping projects due to their strength and versatility.
Road Construction and Pavement Reinforcement
Weak subgrade soils can cause pavement cracking, rutting, and premature deterioration. Geotextil tejido placed between the subgrade and base layer distributes traffic loads efficiently, improving pavement performance and extending its service life.
Retaining Walls and Slopes
Retaining walls and slopes are subject to constant geotextil tejido lateral soil pressure. Using woven geotextiles reinforces the soil, reduces lateral stress, and prevents erosion, resulting in safer and more durable structures.
Embankments and Bridges
Geotextil tejido is particularly useful for embankments supporting bridges, highways, and other infrastructure. It enhances load-bearing capacity, minimizes settlement, and improves the stability of heavy-load structures.
See also: The Rise of E Wallet in Modern Transportation
Environmental Protection and Erosion Control
In areas prone to erosion, woven geotextiles stabilize soil while allowing water to pass through. They are commonly used in riverbanks, shorelines, and environmentally sensitive areas to reduce soil loss and protect the ecosystem.
Installation Best Practices
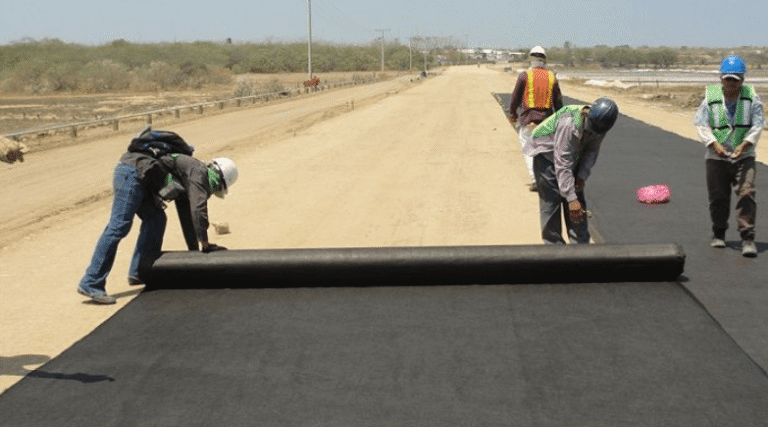
Correct installation is crucial for ensuring the effectiveness of geotextil tejido. Poor placement or preparation can compromise performance and shorten the lifespan of the project.
Site Preparation
Clear the area of debris, roots, and sharp objects. A level, smooth surface ensures maximum contact between the geotextile and soil, enhancing its reinforcement capabilities.
Proper Placement and Overlap
Lay the geotextile flat, with sufficient overlap between sheets to prevent soil migration. Secure anchoring is necessary to maintain the fabric in place during backfilling and compaction.
Backfill and Compaction
Use clean, well-draining backfill material to maintain effective drainage. Gradual compaction prevents overloading the geotextile, allowing it to perform optimally while stabilizing soil layers.
Durability and Long-Term Benefits
Geotextil tejido is resistant to moisture, chemical exposure, and biological degradation. When properly installed and protected from sunlight, it can perform effectively for decades. This durability reduces maintenance costs and supports sustainable construction practices.
Cost Efficiency and Long-Term Value
While the initial cost of geotextil tejido may be higher than traditional methods, it provides significant long-term savings. Reinforced soil structures require fewer repairs, have longer service life, and maintain stability under environmental and mechanical stress. Optimized load distribution can also reduce the need for additional construction materials.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
To ensure optimal performance, avoid the following installation mistakes:
• Selecting the wrong type of geotextile for the project
• Poor site preparation
• Insufficient overlap or inadequate anchoring
• Using low-quality backfill or over-compacting soil
Following proper design and installation standards guarantees the material performs as intended.
Environmental Advantages
Geotextil tejido helps control erosion and sediment runoff, protecting surrounding land and water bodies. Long-lasting installations reduce material waste and promote environmentally responsible construction practices.
Conclusion
The stability and durability of soil-supported structures rely on proper reinforcement, drainage, and load management. Geotextil tejido strengthens soil layers, distributes loads efficiently, and allows controlled water flow. Its high strength and durability make it suitable for roads, slopes, retaining walls, embankments, and environmentally sensitive areas.
When installed correctly, geotextil tejido provides reliable, cost-effective, and long-lasting performance. Incorporating this material into construction and landscaping projects results in resilient structures capable of withstanding environmental and mechanical stresses for decades.